CS49J Lesson 23 – Linkedlist
Ch 15: 15.2

When you come in
- Connect to the Internet
- Log in to Piazza
- Start Eclipse or your IDE
- Navigate to laughton.com/obrien/sjsu/
cs49j/lessons and open this lesson
Ch 15: 15.2

A data structure used for collecting a sequence of objects that allows efficient addition and removal of elements in the middle of the sequence
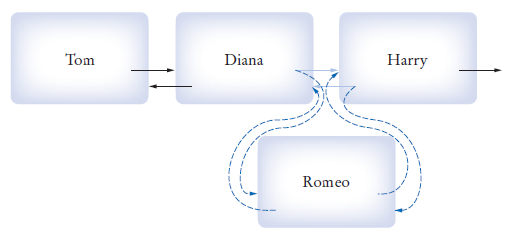
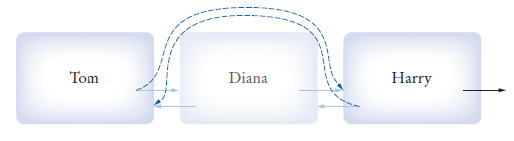
LinkedList<Student> myClass = new LinkedList<>() LinkedList<String> names = new LinkedList<>()
Record your participation in Piazza clicker question Lesson23 Q1
Which of these methods does a LinkedList inherit from Collection interface? Check all that apply. (section 15.1)
Record your participation in Piazza clicker question Lesson23 Q2
Which of these methods does a LinkedList also implement? Check all that apply. (section 15.2.2)
Record your participation in Piazza clicker question Lesson23 Q3
LinkedList<String> flowers = new LinkedList<>();
flowers.addFirst("petuntia");
flowers.addFirst("poppy");
flowers.addLast("zinnia");
flowers.addFirst("pansy");
flowers.add("rose");
String myFlower = flowers.removeFirst();
System.out.println(flowers + " " + myFlower);
Look at this code segment. Assume LinkedList has been imported. What is printed?
You use a ListIterator to access elements inside a LinkedList
To get a ListIterator, use the listIterator() method of the LinkedList class
LinkedList<String> flowers = new LinkedList<>() ... ListIterator<String> iterator = flowers.listIterator();

As an example, you can remove all nodes in the list that meet a condition.
Assume you have a ListIterator called iterator
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String name = iterator.next();
if ( some condition is met)
{
iterator.remove();
}
}
Record your participation in Piazza clicker question Lesson23 Q4
Start with this code. You will use iterator.next() to move through the list
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class LinkedListIterator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Make the list
LinkedList<String> flowers = new LinkedList<>();
flowers.add("rose");
flowers.add("zinnia");
flowers.add("pansy");
flowers.add("petunia");
flowers.add("daisy");
flowers.add("California poppy");
//put your code here
//print the LinkedList
System.out.println(flowers);
System.out.println("Expected: [zinnia, orchid, petunia, Marigold, California poppy]");
}
}